Global economic landscape
New international economic, financial, and political systems emerge as the impact of the New Development Bank and China-driven investments is growing, the power of multinational corporations and non-state actors increases, and a new global consciousness is emerging.
Despite the economic turmoil of 2008, the links forged by technology have continued uninterrupted and even accelerated, ushering in a dynamic new phase of globalization, creating new opportunities, but also triggering unexpected volatility.
- Instead of a series of lines connecting major trading hubs in Europe and North America, the global trading system has expanded into a complex, intricate, sprawling web. These types of connections have paused during the economic turmoil of 2008 and have recovered only slowly since.
- The world trade system is under attack with trade wars of some major; spiral of additional tariffs could lead to severe disruptions in global value chains and in the longer-term to reduce growth prospects.
- Asia recorded the highest regional trade growth from 2008 to 2018. The intra-regional trade rises as emerging economies’consumption is increasing strongly. In 2018, its trade flows were 1.5 times higher than its 2008 levels. China, Viet Nam and India were the most dynamic traders among all Asian economies; “South-South” trade represented an estimated US$ 4.28 trillion or 52% of total developing economies’ exports in 2018. | Related Megatrends: Demography; Consumerism
- China and the EU account for about 50% of global trade. Europe is China’s largest trading partner and China is Europe's primary source of imports. Europe’s annual foreign investment flows with China have been about double of those of the USA.
| Related Megatrends: Inequality; Demography - Several EU countries express concerns about China’s acquisitions of hi-tech European companies, mostly of dual-use technologies.
| Related Megatrends: Technology; Security - An important factor in growing Asian exports are the low labour costs. However, some 58% of the 45.8 million people estimated by the Global Slavery Index to be subject to some form of modern slavery in 2016 globally, are living in 5 Asian countries: India, China, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Uzbekistan. Nevertheless, the labour cost arbitrage is declining in its relevance in the trade of goods; it is currently relevant for less than 20% of goods trade.
| Related Megatrends: Inequalities; Security - World trade of services is more dynamically growing than the one of goods. Global trade in services could increase by 50% by 2040. Emerging economies, like China, India, Brazil are becoming faster service-based than advanced ones. Rising income drives the consumption of knowledge-intensive services that are still highly concentrated in advanced economies. Climate change can disrupt services, like in tourism, and increases the demand of environmental services. Digital technologies will drive global trade of services even further. Demographic change determines the need for education, digital services, health. Related Megatrends: Technology; Consumerism; Inequality; Demography
- China-Africa trade increased more than 200 times over the past 40 years -- ftom USD$765 million in 1978 to USD$170 billion in 2017, gaining another 17.7% in the first part of 2018.
-
The African continent could mimic China’s rapid raise over the next 50 years, if structural reforms to overcome institutional lethargy and corruption will continue and accelerate. The further integration of the African Union to a borderless Africa could unleash a USD2.5 trillion African economy. 24 million people more will live in cities each year between 2015 and 2045, that will increase consumption. Africa showed already its potential to fully exploit the potential of new technologies, e.g. with rapid adaptation of mobile phones or mobile banking, or drones to deliver medical facilities or blood in remote areas of Rwanda (“Zipline”) – new digital technologies could deliver innovative solutions for core challenges in Africa. STEM education initiatives contribute to building the needed capabilities.
| Related Megatrends: Urbanisation; Consumerism; Demography; - Chinese aims to become world leader in science and innovation by 2050. In 2017, China's R&D spending was about $378.6 billion (PPP), accounting for 21% of total world R&D expenditure, with the rate of R&D investment growth significantly exceeding that of the U.S. and the EU.
- India's digital sector might be a $1 trillion economy by 2023. Some 50% of the country's 1.25 billion people, 600 million are under 25 years old, while 65% is 35 or younger.
| Related Megatrends: Consumerism; Demography; Technology;
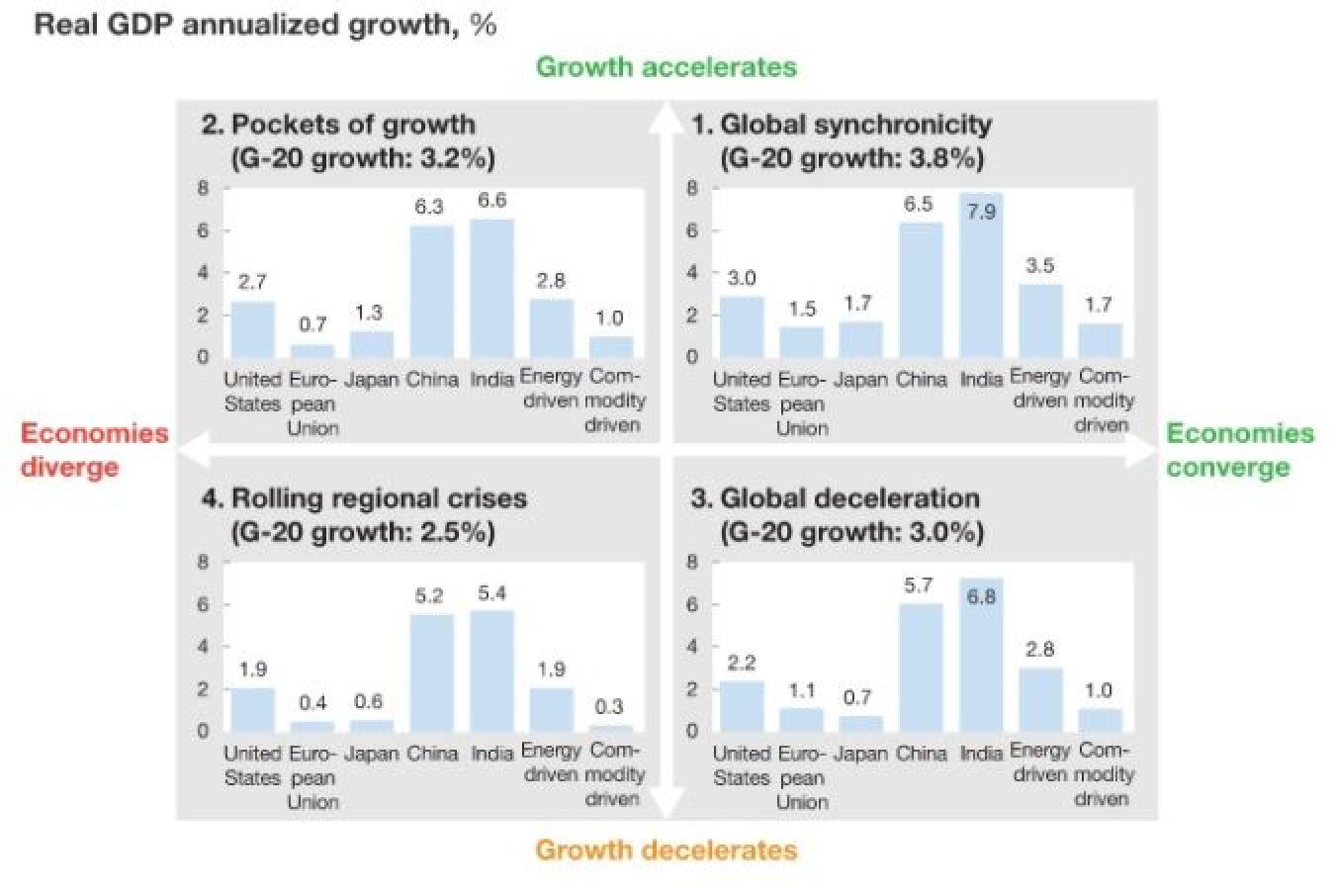
- The rate of economic growth of Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDE) is over 4% (China and India around 7%), while that of the advanced economies is around 2% (in the euro area projected at 1.8% in 2017 and 2018). | Related Megatrends: Demography; Consumerism
- Asia is the world’s largest trading region and with the highest continuous rate of growth; “South–south” flows between emerging markets have doubled their share of global trade over the past decade. | Related Megatrends: Demography; Consumerism
- India has 600 million people (50% of the country's 1.25 billion population) under 25 years old; 65% of its population is 35 or younger. Their capacity and needs will have considerable impact in shaping the outcomes of elections and the country's future.| Related Megatrends:Demography; Consumerism; Governance; Education
- An important factor in growing Asian exports are the low labour costs. However, some 58% of the 45.8 million people estimated by the Global Slavery Index to be subject to some form of modern slavery in 2016 globally, are living in 5 Asian countries: India, China, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Uzbekistan. | Related Megatrends: Inequalities
- By 2030, Asia might surpassed North America and Europe combined in terms of global power, given its higher rate of economic growth, larger population, increasing military spending, and growing technological investment. China alone will probably have the largest economy, surpassing that of the United States a few years before 2030. Meanwhile, the economies of Europe, Japan, and Russia are likely to continue their slow relative declines.
- Global FDI flows decreased by 20% in the first half of 2019 to USD 572 billion. FDI inflows to non-OECD G20 economiesincreased by 21% and FDI outflows remained stable.
- China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a geopolitical development strategy to build connectivity and co-operation across six main economic corridors from China to Mongloia and Russia; to Eurasian countries; to Central and West Asia; to Pakistan and other countries of the Indian sub-continent; to Indochina. BRI investments projects are estimate over USD 1 trillion outward funding for foreign infrastructure from 2017 to 2027.
- The China International Development Cooperation Agency (CIDCA) established in 2018 to oversee China's increasing foreign aid and investment activities launched the China-Africa Cooperation Action Plan (2019-2021) that includes multi-billion dollars projects covering all spheres -- from agriculture and food safety to IT, infrastructure and social development cooperation.
- China became the single largest contributor of foreign direct investment in Africa in 2014-2018, having invested USD$72.2 billion (more than double of FDIs from France or USA), thus creating 137 throusand jobs.
- The China Development Bank and Eximbank have provided some $150 billion in finance to Latin America and the Caribbean since 2005 (when Chinese banks began lending to the region) and the Chinese state-to-state finance surpasses that from the World Bank, Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), and Andean Development Bank (CAF).
- Chinese FDI and aid are not governed by the the Paris principles; they don't require improved governance, nor respect of human rights, nor combating corruption. There seems to be not even a clear distinction between grants, loans and aid.
- Over the past decade, Europe’s annual foreign investment flows with China have been about double of those of the USA, although starting at about the same level.
- Several EU countries express concerns about China’s acquisitions of hi-tech European companies, mostly of dual-use technologies.
| Related Megatrends: Technology; Security
China
- Hong Kong has more than 10,000 residents who each control at least $30 million — about a 31% jump from 2016 to 2017.
The ranks of the ultrarich have also increased by double-digits over the last five years in quickly growing southeast Asian countries, such as Bangladesh, India and Vietnam. - China reduced its rural poverty from 130 million to 30 million people and intends to eliminate absolute poverty by 2021 (in 2018 alone, it will lift 10 million people from absolute poverty). | Related Megatrends: Inequalities; Consumerism
China's R&D
- China aims to become world leader in science and innovation by 2050. "Made in China 2025" announced in 2015, outlines China's strategy to become a world leader in a number of high-tech industries, such as robotics, aerospace equipment, medical devices, and more.
- In 2017, China's R&D spending was about $280 billion, accounting for 2.12% of the country's GDP and representing 20% of total world R&D expenditure, (on par with Europe (34 countries)) with the rate of R&D investment growth significantly exceeding that of the U.S. and the EU. Expressed in PPP, China's investment in R&D was $370.6 billion in 2017, second to the $476.5 billion of the USA.
| Related Megatrends: Technology; Inequalities - Based on its R&D and industry strategy, China has become competitor in fast growing high-tech sectors, like nuclear energy, new energy vehicles, wind and solar PV, Artificial Intelligenc and some parts of advanced manufacturing and robotic (drones).
- Over the past 15 years, China has tripled its high-impact scientific efforts (as measured by its share of top 10% most-cited publications), reaching 14% – the second largest scientific powerhouse after the United States (that has 25%). | Related Megatrends: Technology
- China has 43% of the unicorn's value (start-ups valued at over $1 billion)
- Since 2016, China has had the most industrial robots in operation globally. The Robotics Industry Development Plan adopted in 2016 aims to accelerate the development of the industrial robotics sector. By 2020, China is expected to produce 150,000 industrial robot units and have 950,300 industrial robots in operation.
| Related Megatrends: Technology; Security; Inequalities - China is set to become the world's largest nuclear power producer by 2030, with a projected installed nuclear capacity increase from 34 GW in 2016 to 111 GW in 2030 and 145 GW in 2040. | Related Megatrends: Natural resources; Consumerism; Climate and environment
Digital power
- China's overall digitalization is medium in the global comparison, but it is global leader in some key industries and with its R&D and industrial strategy it strives for global leadership in further area.
- China plans to be world leader in AI by 2030. China has the top 3rd and 4th most powerful supercomputers.
- China’s digital economy becomes a leading global force. China has:
- 731 million Internet users, more than the EU and the USA combined
- 44% of worldwide M2M (machine-to-machine) sim card subscriptions (three times the share of the United States)
- the world’s largest e-commerce market - accounting for over 40% of the global e-commerce transactions' value (from less than 1% about a decade ago)
- China accounts for 32% of global ICT goods exports
- the most active digital-investment and start-up ecosystems in the world, mainly active in big data, AI, and fintech
- mobile payments' value 11 times that of the USA (some 68% of Chinese Internet users are making mobile digital payments, compared with only around 15% in the USA)
- the big digital power BAT (Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent) provided 42% of all venture-capital investment in China in 2016 (compared to 5% by Amazon, Facebook, Google, and Netflix in USA) and - other digital innovators such as Xiaomi, NetEase and Ping An are also building their own ecosystems.
- | Related Megatrends: Technology; Security; Governance
- the Chinese 5G network equipment industry, got into a global trade war with the US blocking Huawei to supply its networks; the US is worried about cyber security vulnerabilities of the critical communication infrastructure that is crucial for industry 4.0 applications. Chinese Huawei is currently seen as a follower with Swedish Ericsson and South Korean Samsung as leaders in the in the 5G infrastructure provider market.
Digital economy
- China’s digital economy becomes a leading global force. China has:
- 731 million Internet users, more than the EU and the USA combined
- 44% of worldwide M2M (machine-to-machine) sim card subscriptions (three times the share of the United States)
- the world’s largest e-commerce market - accounting for over 40% of the global e-commerce transactions' value (from less than 1% about a decade ago)
- 43% of the unicorn's value (start-ups valued at over $1 billion)
- the most active digital-investment and start-up ecosystems in the world
- mobile payments' value 11 times that of the USA (some 68% of Chinese Internet users are making mobile digital payments, compared with only around 15% in the USA)
- the top two most powerful supercomputers in the world.
| Related Megatrends: Technology - the big digital power BAT (Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent) provided 42% of all venture-capital investment in China in 2016 (compared to 5% by Amazon, Facebook, Google, and Netflix in USA) and - other digital innovators such as Xiaomi, NetEase and Ping An are also building their own ecosystems.
| Related Megatrends: Technology; Security; Governance
Media
- The merger of main Chinese state media (China Central Television (CCTV), China Radio International and China National Radio) into one "Voice of China" is consolidating Chinese state media power and the message it wants to disseminate, but is questioning even more democracy. | Related Megatrends: Governance
| Originally Published | Last Updated | 06 Sep 2018 | 11 Oct 2018 |
| Knowledge service | Metadata | Foresight | The Megatrends Hub | Expanding influence of east and south |
| Digital Europa Thesaurus (DET) | globalisationgovernanceinternational ocean governancepopulation censuspovertydigital transformation |
Share this page