The EU is convinced that investing in improving nutrition is one of the most effective investments to improve children’s health and education, and the development of the community. The EU has demonstrated a global leadership role with respect to a steadfast focus on a rights-based, multi-sectoral, country-led and locally driven approach to tackling malnutrition. In doing so, the EU has also set itself some ambitious targets:
- To support countries in reducing the number of stunted children under the age of five by at least 7 million by 2025 (a commitment made in 2012);
- To allocate EUR 3.5 billion between 2014 and 2020 on nutrition interventions to help reduce stunting (a commitment made in 2013);
- In December 2021, at the Nutrition for Growth (N4G) Summit in Tokyo, and for the period 2021-2024, the EU pledged to commit a further EUR 2.5 billion for international assistance with a nutrition objective.
These commitments are institutionalised within the EU’s policy framework on nutrition:
- the 2013 Commission Communication Enhancing Maternal and Child Nutrition in External Assistance;
- the associated Council Conclusions of May 2013;
- the EU Action Plan on Nutrition (2015-2025) setting out the way the Commission will deliver on its stunting target.
The EU’s focus on women, children and adolescent girls and the 1000-day window of opportunity are being realised under each of the three strategic priorities outlined in the Nutrition Communication and Action Plan:
- Strategic priority 1: Enhance mobilization and political commitment for nutrition
- Strategic priority 2: Scale up actions at country level
- Strategic priority 3: Knowledge for nutrition
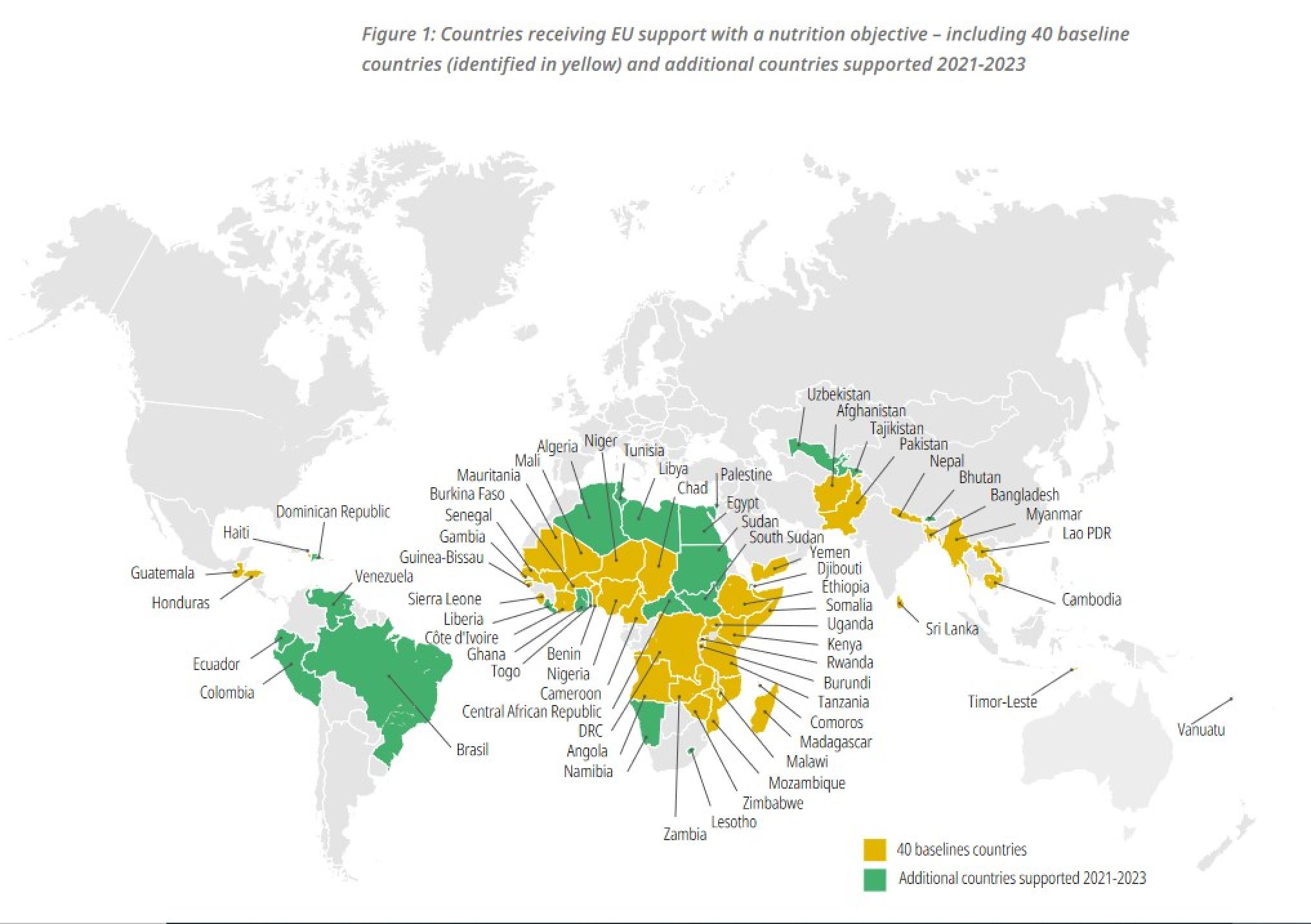
To maximise the impact of the Action Plan on Nutrition, the European Commission had identified 42 countries of strategic priority for its support to nutrition (2014-2020). These countries had (i) a high burden of stunting (ii) a politically committed government; and (iii) requested support from the EU Delegations to address undernutrition.A review of newly adopted country level multi-annual indicative programmes (MIPs, 2021-2027) indicates that a growing number feature nutrition or healthy diets under at least one priority area.
An important channel for the financing of food and nutrition security is the Thematic Programme on Global Public Goods and Challenges and its Food and Nutrition Security Action Area (see the latest Implementing Decision).
There are annual reports highlighting the progress the EU and its Member States have achieved towards the Commission's commitments on nutrition.
With the new programming cycle for 2021-2027 now under implementation, the eighth progress report provides an opportunity for closure with respect to the EU’s ambitious 2013 pledge. This report indicates that by 2024 the EU had committed over EUR 4.4 billion with a nutrition objective, EUR 1.9 billion more than was originally pledged.
The EU is currently on track to assist partner countries to reduce the number of stunted children by 7 million by 2025.
The renewed pledge for international assistance with a nutrition objective ensures continuity in the efforts to make progress to reduce the number of stunted children under the age of five by at least 7 million by 2025.
One major focus of the EU effort has been in providing support to the Scaling-Up Nutrition (SUN) movement, which is a unique initiative to strengthen inter-sectoral and inter-stakeholder cooperation by emphasizing the pivotal role of national governments leaderships. In addition, support is being provided to the Global Nutrition Report as a critical contribution to global accountability in nutrition.
The communications “Farm to Fork Strategy”, “Rights of the Child” and “Towards a Comprehensive Strategy with Africa” confirms EC willingness to boost cooperation to improve nutrition and alleviate food insecurity through resilient, safe and, sustainable food systems.
Direct EU engagement in eight Coalitions for Action emerging from the UN Food Systems Summit further testifies to the EU’s unceasing leadership role in accelerating transformative efforts to ensure healthy and sustainable diets for all and the eradication of malnutrition in all its forms.
- Explore EU policies related to "Nutrition"
- Explore EU projects related to "Nutrition"
- Explore EU Research and innovation activities on "Nutrition"
You can explore EU commitments on nutrition in several countries in the 'EU commitments on nutrition tab' of the country dashboards.
| Originally Published | Last Updated | 11 Apr 2019 | 19 Mar 2025 |
| Knowledge service | Metadata | Global Food and Nutrition Security | Nutrition |
