Hunger and food insecurity have continued to increase in the Arab region due to various factors, including the COVID-19 pandemic.
Part 1 of this report will present the latest detailed statistics on the region’s food security and nutrition situation.
The number of undernourished people reached 54.3 million in 2021 or 12.2 percent of the population.
Moderate or severe food insecurity affected an estimated 154.3 million people in 2021, up from 142.7 million in 2020 – an increase of 11.6 million.
Furthermore, the region continued to suffer from multiple forms of malnutrition, including stunting, wasting, overweight among children and obesity among adults.
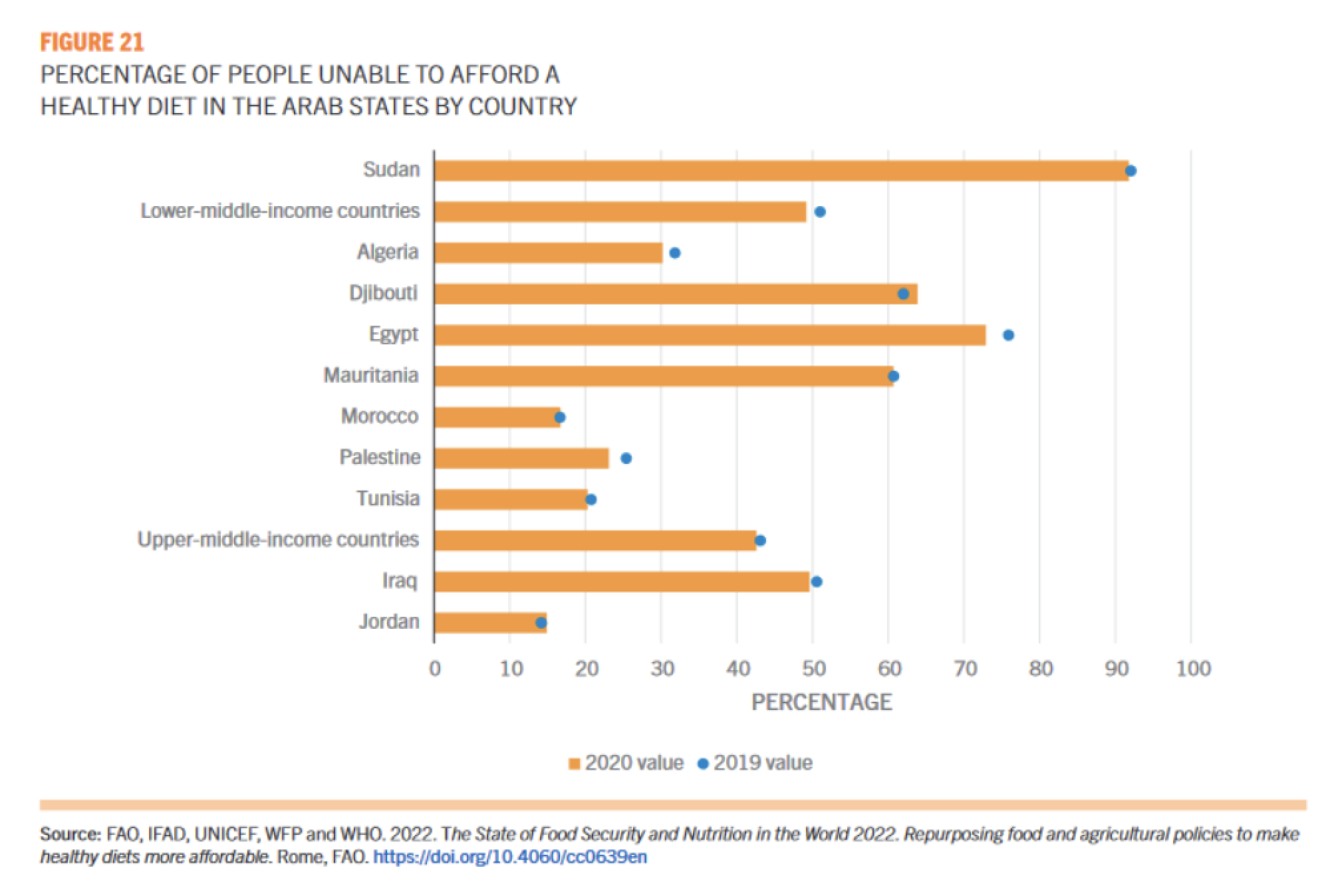
More than half the population in the Arab States, or 162.7 million people, could not afford a healthy diet in 2020.
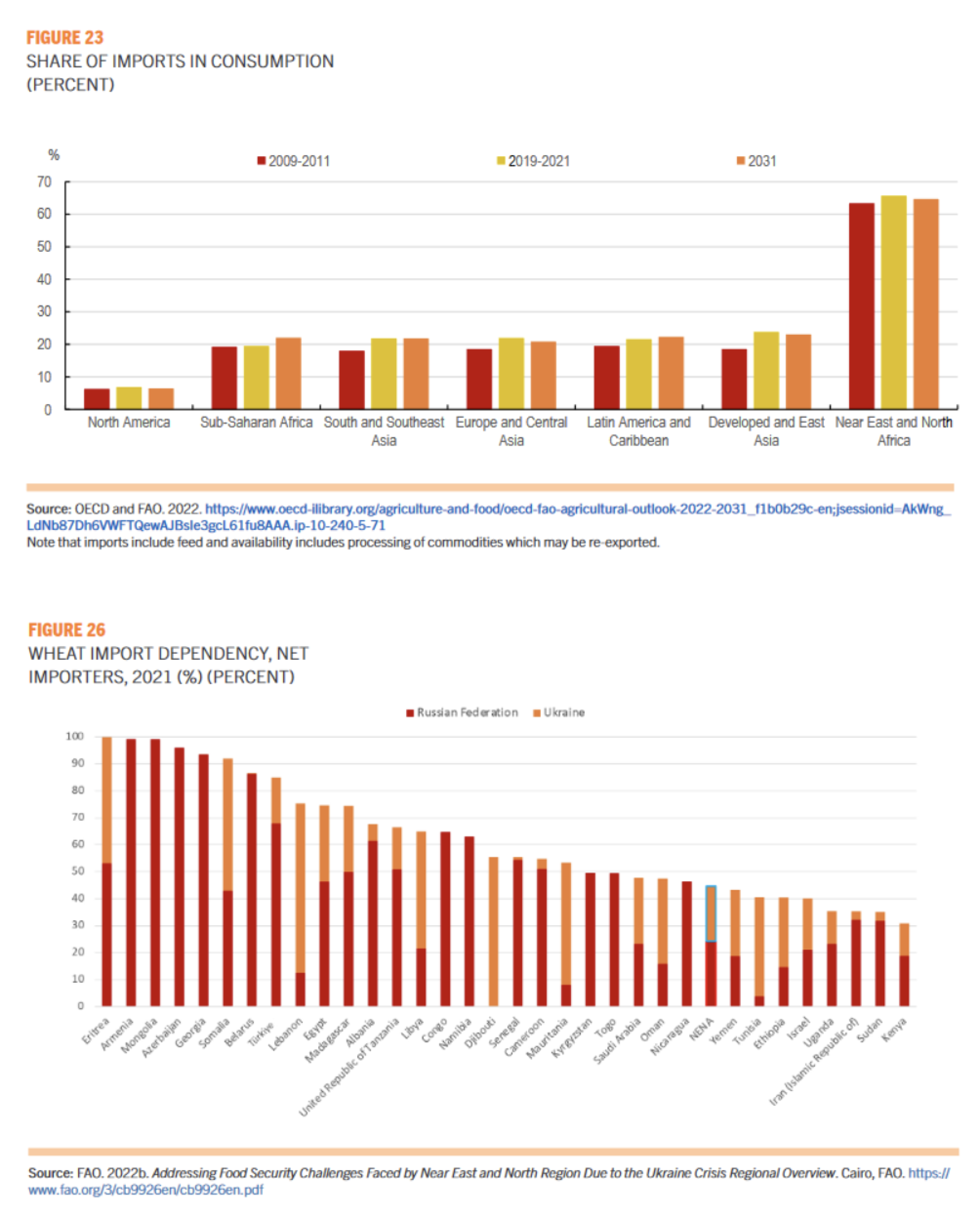
The war in Ukraine and its effects on international agrifood markets with supply shocks and increasing global food and energy prices are further exacerbating the food security and nutrition challenges of the region, which is highly dependent on imported foodstuffs, including wheat and fertilizers from the Black Sea region.

Part 2 showed that trade presents a significant opportunity as an enabler to achieving the four dimensions of food security and supporting progress towards achieving the SDGs.
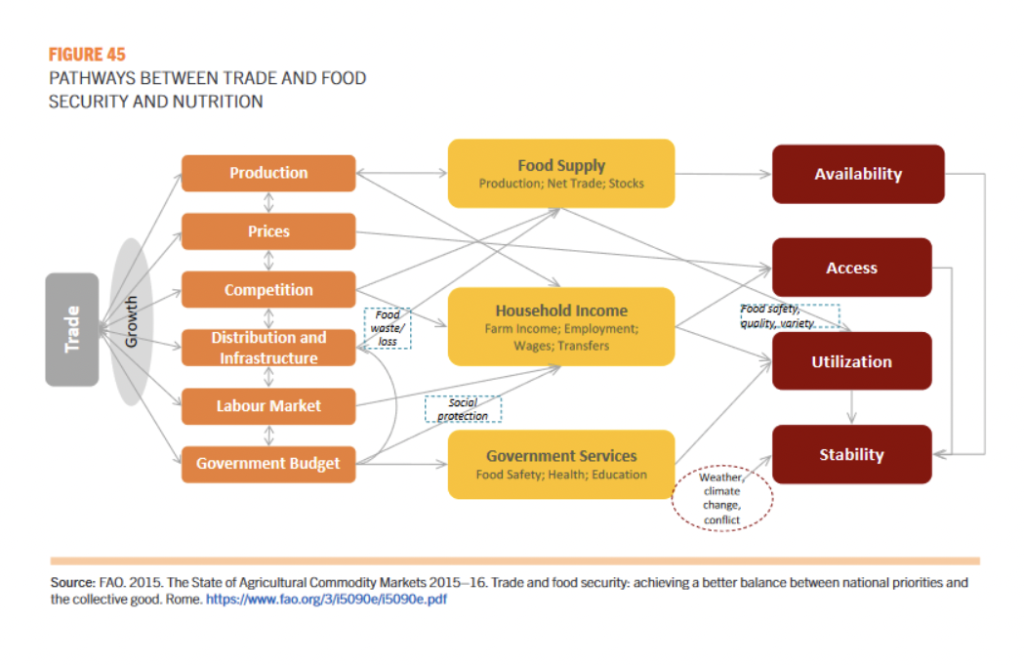
Trade allows for an adequate supply of diversified food to all countries, especially those with constrained domestic production, and helps countries to overcome constraints in land and water endowments.
On the other hand, as Arab countries are dependent on international food markets, they are more exposed to shocks, as highlighted by the COVID-19 pandemic and war in Ukraine. For the region, managing international trade connectivity is critical to reducing exposure to external shocks.
After carefully assessing strengths, weaknesses and gaps, the following key considerations should be taken as a means to enable agrifood systems transformation in the region that leverages trade and investment.
-
The role of trade as an enabler for food security could be achieved by harnessing the potential of intra-regional trade, including progressive liberalization of tariffs on agriculture and food products. However, tariff reduction should consider small-scale food producers, who might be exposed to increased international competition due to reductions in tariffs. Progressive trade liberalization supported by other policies, such as social safety net measures, can address such vulnerabilities. In addition, managing international trade connectivity in a resilient manner is critical to reducing exposure to external shocks. National agrifood systems supplying food from diversified import sources are more flexible and resilient to supply shocks.
-
Arab countries must leverage intra-regional trade and rely more on each other’s capacities. One lesson of the recent food supply chain disruptions has been to rely more on regional trade when there are surpluses in one country and shortages in another to avoid shocks and ensure food security, especially for the countries that are most heavily reliant on food imports. To support environmentally sustainable, nutritious, safe and inclusive agrifood systems, countries should jointly pursue trade agreements that reinforce non-market values, such as food safety, environmental quality or nutritional content as well as decent labour conditions.
-
Arab countries must also strengthen their governance, human capital and institutions.They need to attract private capital to increase their participation in global value chains and regional and global trade.
-
Improving governance and policy coherence between trade and other sectors has become increasingly important. Trade and related policies to support the implementation of agricultural strategies and investment plans are essential to achieving food security and nutrition objectives.
-
Each country needs to consider their specific conditions and to understand better and minimize the trade-offs between competing policy objectives.
-
Conservation of nature and climate resilience. Due to minimal natural resources, some countries must conserve and sustainably manage natural resources and increase resilience to climate change. The region needs to consider the implications of any policy on climate change and environmental sustainability. This requires an agrifood systems approach that considers the broader implications of sectoral policies on several sustainability outcomes.
-
Food loss and waste. Reduced food loss and waste, increased economic value of food trade, increased income opportunities and reduced health risks for the more vulnerable population are all benefits of policies and regulations preventing food loss/waste and maintaining the quality of food traded from the farm to the shop through best practices.
-
Countries in the area could start rethinking how they can reallocate their existing public budgets to make them more cost-effective and efficient in reducing the cost of nutritious foods and increasing the availability and affordability of healthy while at the same time considering and tackling the food security and environmental challenges in the NENA region.
-
International trade enhances technology and knowledge spillovers that can increase productivity, improve employment opportunities and raise incomes. Many countries in the region should leverage innovative technologies and approaches to transform agrifood systems, putting young people at the center of this effort.
-
Trade should be inclusive. Its benefits should be distributed equally across and within countries and contribute to gender equality. New trade opportunities must be complemented with measures that contribute to women’s economic empowerment and higher wages for women.
| Year of publication | |
| Authors | |
| Geographic coverage | RomaniaSaudi ArabiaYemenUnited Arab EmiratesSudanTunisiaMauritaniaMoroccoDjiboutiComorosAlgeriaEgyptKuwaitJordanIraqLebanon |
| Originally published | 05 Apr 2023 |
| Related organisation(s) | FAO - Food and Agriculture Organization of the United NationsWFP - World Food ProgrammeWHO - World Health OrganisationUNICEF - United Nations Children's FundIFAD - International Fund for Agricultural Development |
| Knowledge service | Metadata | Global Food and Nutrition Security | Food security and food crises NutritionCOVID-19 and Food and Nutrition Security | Food and nutrition securityCost of the dietFood price crisisFood supply chainHealthy diet |
| Digital Europa Thesaurus (DET) | war in Ukraineregional integrationprice of agricultural produceagricultural tradeclimate change policypolicymaking |
