The European Commission Knowledge Centre on Earth Observation (KCEO) has finalised the second Deep Dive assessment addressing Urban Climate Adaptation, which examines how Earth Observation (EO) products and services can assist EU Policies on Urban Climate Adaptation.
The KCEO Urban Climate Adaptation Deep Dive evaluates the requirements of EU policies regarding urban climate adaptation, determines how well existing EO products and services address these needs, identifies gaps, and suggests directions for future developments of Copernicus products and services.
Objectives
The Urban Climate Adaptation Deep Dive report, the second of a series of deep dive assessments of the KCEO examines how EO products and services can assist in urban climate adaptation policies. Specifically, it evaluates the requirements of EU policies regarding urban climate adaptation, determines how well existing EO products and services address these needs, identifies gaps, and suggests directions for future developments of Copernicus products and services.
Components of the assessment include the needs of EU policy; a consolidated set of EO-relevant urban climate adaptation indicators; considerations on the relevance of Horizon Europe Missions and a series of use cases spanning urban heat islands, urban greening, water management, urban coastal risks and adaptation, and urban development in Africa co-developed co-designed together with a number of European Commission Directorates-General. A common set of adaptation measures is represented by the Key Type Measures adopted by European Environment Agency.
Policy context
The report addresses the policy- and decision-making needs of the 2021 EU Adaptation Strategy, European Green Deal, European Climate Law, the National Adaptation Plans of Member States, and local actions under e.g., the Covenant of Mayors Framework.
It is a collaboration with relevant Directorates-General (DGs) of the European Commission and Copernicus Entrusted Entities, particularly the European Environment Agency (EEA).
Key outcomes of the study
Earth Observation already plays an important role in informing urban adaptation, but it is significantly under-exploited due to an under developed value chain and could be used to much greater effect in the design, monitoring, and evaluation of European and global adaptation actions.
Substantial ongoing European adaptation investments would greatly benefit from the improved availability of EO-derived, standardised, actionable intelligence tools and policy-facing compound indicators that address national and municipal scales, complemented by actions to improve community uptake and user-based intelligence optimisation.
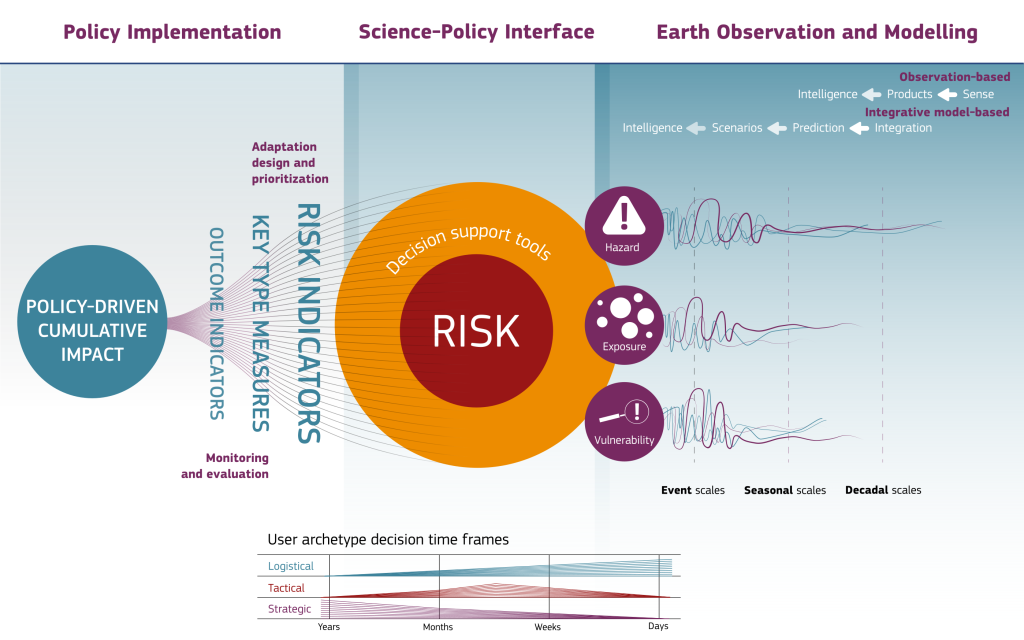
A key innovation presented here is the Earth Observation Value Chain Framework shown below, illustrating how intelligence can be derived and synthesised using a hazard-vulnerability-exposure nexus to address a variety of user needs, culminating in cumulative policy impact.
The Framework shows the importance of moving beyond the current emphasis on climate hazard information, foregrounding vulnerability and exposure metrics as key dynamic continuum parameters and providing intelligence focusing on derived combined risk or more highly synthesised compound indicators addressing outcomes and adaptation impact.
Recommendations relevant from policy to EO and modelling include:
Enabling policy-focused use of standardised, quantitative EO-derived adaptation indicators for legislative uptake in Member States and the European Commission
Developing & supporting an adaptation intelligence community
Development of highly synthesised intelligence services providing actionable information to key user archetypes
Establishment of a Thematic Hub for Urban Climate Adaptation
Facilitate and implement capabilities for city-based adaptation scenario modelling
Provision of automated change detection products and services to identify combined risk changes
Facilitate the use of Destination Earth to develop more actionable intelligence and cater for policy-relevant audiences with “last-mile” applications
Provision of dynamic hazard-specific combined risk products and services across a range of time scales
Optimised integration of EO-derived intelligence with Eurostat and socioeconomic data
Expansion of Copernicus urban-relevant services to global
Systematic acquisition and integration of very high-resolution optical imagery for urban area intelligence
Publication

Urban areas as major population centres are inherently exposed to high and compound climate risks, impacting across a socioeconomic, ecological, financial, and political nexus. The EU policy landscape recognises the critical importance of urban climate adaptation, as encompassed by the European Green Deal, EU Climate Adaptation Strategy, and European Climate Law. A key aspect of achieving the policy objectives is using knowledge and intelligence derived from Earth Observation (EO) to enable smarter, faster, and more systemic adaptation. This report presents the findings of the second deep dive assessment of the Knowledge Centre on Earth Observation (KCEO), focusing on how EO products and services can support EU policies on urban climate adaptation. Components of the assessment include the needs of policy and Horizon Europe Missions; a consolidated set of EO-relevant urban climate adaptation indicators; and a series of use cases spanning urban heat islands, urban greening, water management, urban coastal risks and adaptation, and urban development in Africa co-developed with several European Commission Directorates-General. A common set of adaptation measures is represented by the Key Type Measures approved by European Environment Agency. Whilst EO provides valuable information for urban adaptation needs, uptake and impact could be significantly improved through higher value intelligence offerings, tailored for decision-making. Relevant recommendations include the development of policy-focused risk and outcome indicators, a greater range of combined risk and change detection services, and city-based adaptation scenario capabilities; enabling user networks of adaptation intelligence communities; and integrating higher spatial resolution products.
| Originally Published | Last Updated | 10 Oct 2024 | 16 Apr 2025 |
| Related project & activities | Copernicus |
| Related organisation(s) | JRC - Joint Research CentreDG DEFIS - DG for Defence Industry and Space |
| Knowledge service | Metadata | Earth Observation |
| Digital Europa Thesaurus (DET) | urban habitatadaptation to climate change |
Share this page
