As part of the initiative on Digital Agriculture Transformation by the World Bank, this Digital Agriculture Profile for Vietnam leverages the expertise of stakeholders to evaluate the current landscape of digital agriculture in Vietnam. This include key players across value chains, the main barriers they face, and the potential to overcome these barriers through the adoption of innovative technologies. In identifying and prioritizing these technologies, this study aims to support investors and users in maximizing their impact by focusing on the opportunities of highest potential. Once enabling factors are identified and understood, the mainstreaming of digital agriculture in Vietnam can truly begin.
HIGHLIGHTS
Agriculture plays a vital role in Viet Nam’s economy, accounting for an average of 17% of the national GDP and employing 40% of the national workforce.
The biggest challenges existing in agri-food system are information gaps, resulting in high transaction costs for various stakeholders to engage in market activities. On-farm, lack of actionable decision-support systems for farmers result in unsustainable use of resources and low productivity levels.
The most promising technologies for addressing these issues include smartphones (that can send and receive information), QR codes, blockchain (that connect information and data across the value chain), cloud-based solutions (that enable storage and access of data and information across varied sources), Internet of things, unmanned aerial vehicles (that facilitate gathering of data and insights at high resolution), and data analytics (that enables conversion of data to information and knowledge products).
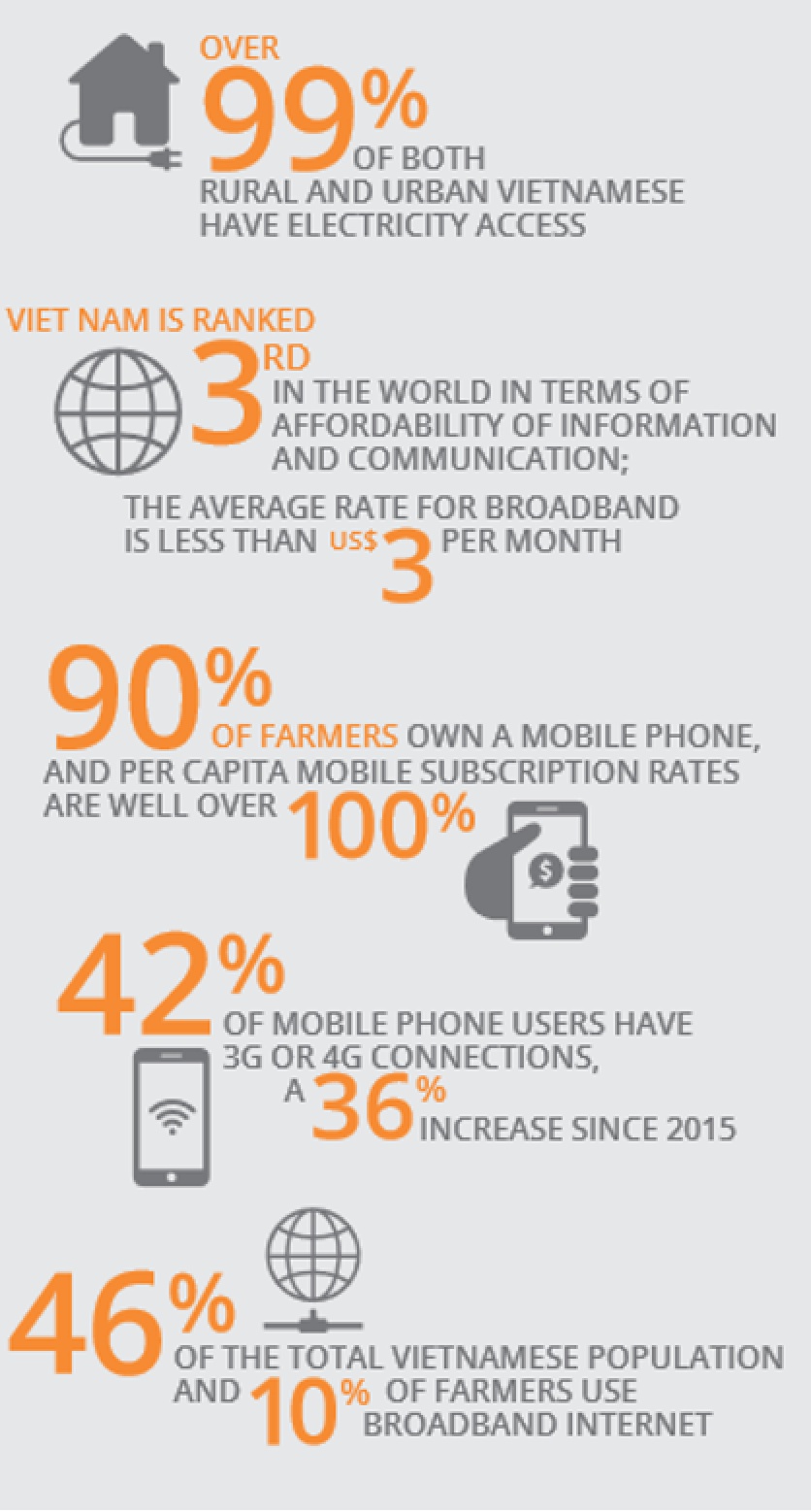
Digital infrastructure is well established in Viet Nam; the primary constraint to digital agricultural solutions is digital illiteracy—i.e., stakeholders’ inability to use digital technologies to acquire information, communicate, and solve challenges in the value chain.
The private industry, public sector, nonprofit organizations, and international community all have important and distinct roles to play in creating sustainable digital agricultural solutions in Viet Nam.
| Year of publication | |
| Publisher | World Bank Group |
| Geographic coverage | Vietnam |
| Originally published | 09 Jul 2021 |
| Knowledge service | Metadata | Global Food and Nutrition Security | Research and Innovation |
| Digital Europa Thesaurus (DET) | Agriculturedigital technologydigital transformation |
