Highlights:
The authors of the report uses recent econometric methodologies to answer the question of how rainfall shocks have affected the economy over time. The analysis was conducted at a high degree of spatial disaggregation to capture the effects of rainfall variations on economic indicators of interest.
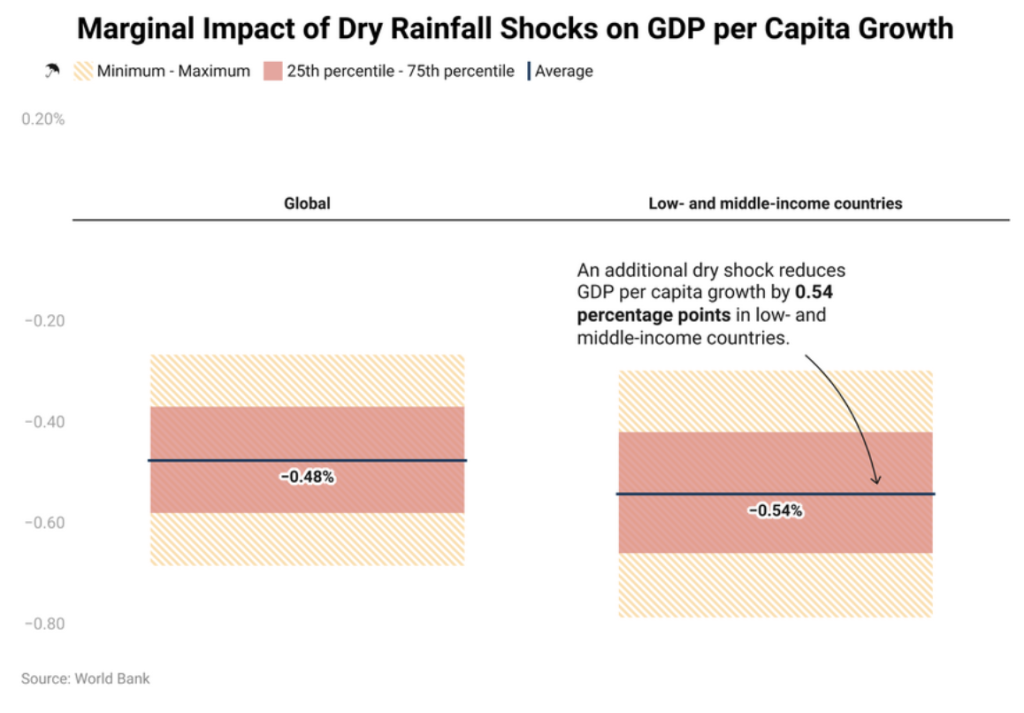
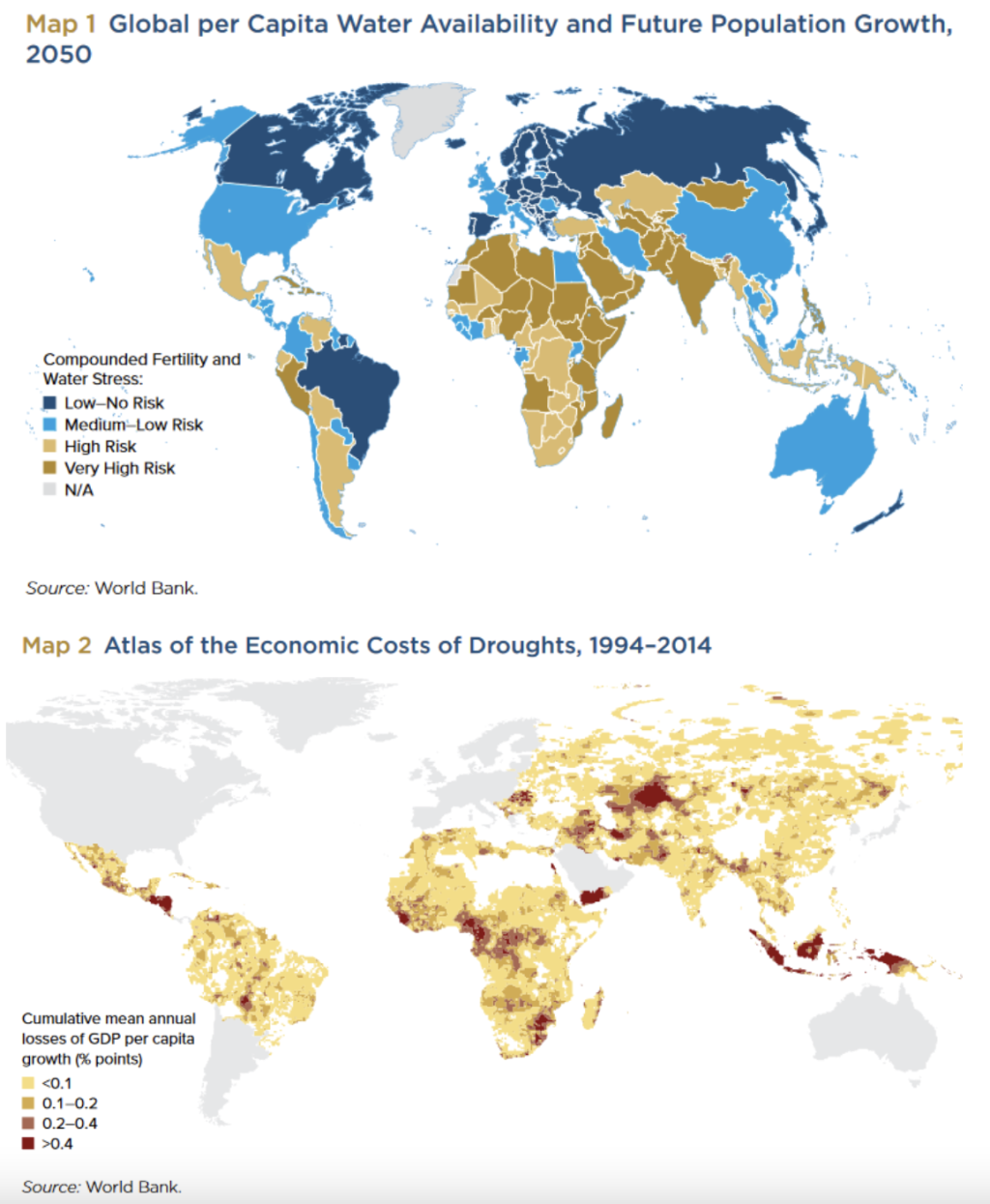
By examining the effects of water on a single aggregate measure -- economic growth -- the report finds that low-income countries and middle-income countries are considerably more vulnerable to dry shocks than are higher-income countries.
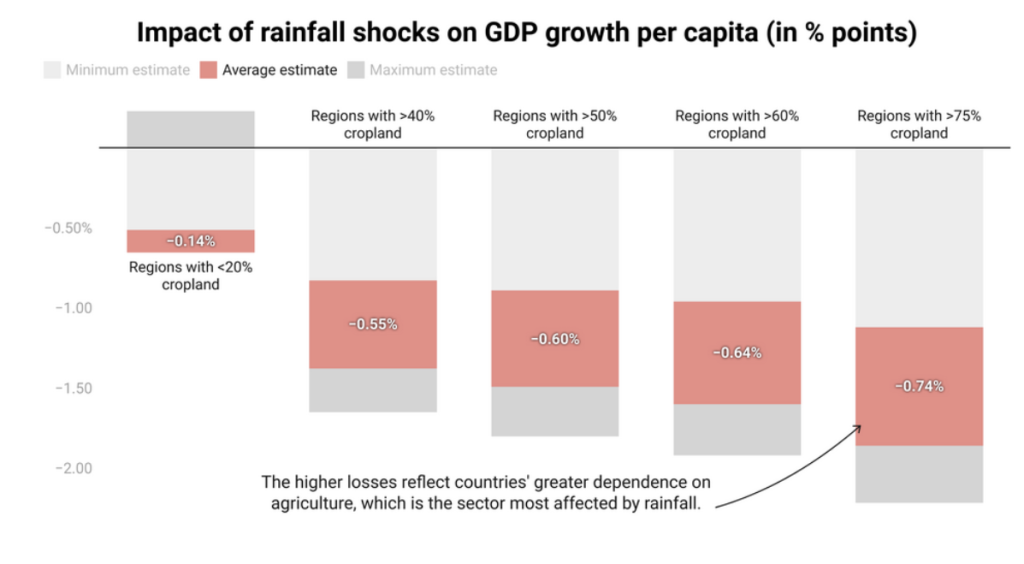
As the severity of a drought increases, so too does the impact on economic growth.
-
In low- and middle-income countries, moderate drought reduces growth by about 0.39 percentage points, and extreme drought reduces growth by about 0.85 percentage points (average growth rate 2.19%).
-
By contrast, in high-income countries, extreme droughts reduce growth by a little less than half the impact felt in developing countries.
The adverse effects on economic growth are therefore sharper in agriculture-dominated areas of the developing world. The higher losses reflect these countries’ greater dependence on agriculture, which is the sector most affected by rainfall disruptions.
The findings have several implications for development practitioners.
Firstly, the authors insist on the significance of green water in mitigating drought impacts, which has been previously overlooked in economic deliberations, cannot be overestimated. The report highlights the need for sound stewardship of forests and other natural capital that affect the hydrological cycle and soil moisture, but are seldom associated with the growth impacts of droughts.
They also highlight the need for proactive investment to address vulnerabilities through upgrades in information systems, institutions, and infrastructure that build drought resilience.
| Year of publication | |
| Authors | |
| Geographic coverage | EswatiniBrazilGlobal |
| Originally published | 15 Sep 2023 |
| Related organisation(s) | World Bank |
| Knowledge service | Metadata | Global Food and Nutrition Security | Climate extremes and food security | Extreme weather event |
| Digital Europa Thesaurus (DET) | droughteconomic growthAgriculturepolicymakingimpact study |
